A domain name is an identification string that defines a realm of administrative autonomy, authority or control within the Internet. Domain names are formed by the rules and procedures of the Domain Name System (DNS). Any name registered in the DNS is a domain name. Domain names are used in various networking contexts and application-specific naming and addressing purposes. You probably have hundreds of domain names stored in your head, such as:
- powerhoster.com — our favorite domain name
- google.com — one of the most used domain names in the world
- mit.edu — a popular EDU name
- bbc.co.uk — a three-part domain name using the country code UK
You’ll recognize domain names as having strings of characters separated by dots (periods). The last word in a domain name represents a top-level domain. These top-level domains are controlled by the IANA in what’s called the Root Zone Database, which we’ll examine more closely later.
In general, a domain name represents an Internet Protocol (IP) resource, such as a personal computer used to access the Internet, a server computer hosting a web site, or the web site itself or any other service communicated via the Internet. In 2015, 294 million domain names had been registered.
Domain names are used to identify one or more IP addresses. For example, the domain name microsoft.com represents about a dozen IP addresses. Domain names are used in URLs to identify particular Web pages. For example, in the URL https://powerhoster.com/index.html, the domain name is powerhoster.com.
A domain name is an identification string that defines a realm of administrative autonomy, authority or control within the Internet. Domain names are formed by the rules and procedures of the Domain Name System (DNS). Any name registered in the DNS is a domain name. Domain names are used in various networking contexts and application-specific naming and addressing purposes. In general, a domain name represents an Internet Protocol (IP) resource, such as a personal computer used to access the Internet, a server computer hosting a web site, or the web site itself or any other service communicated via the Internet. In 2015, 294 million domain names had been registered.
Every domain name has a suffix that indicates which top level domain (TLD) it belongs to. There are only a limited number of such domains. For example:
Because the Internet is based on IP addresses, not domain names, every Web server requires a Domain Name System (DNS) server to translate domain names into IP addresses.
Because all of the names in a given domain need to be unique, there has to be some way to control the list and makes sure no duplicates arise. That’s where registrars come in. A registrar is an authority that can assign domain names directly under one or more top-level domains and register them with InterNIC, a service of ICANN, which enforces uniqueness of domain names across the Internet. Each domain registration becomes part of a central domain registration database known as the whois database. Network Solutions, Inc. (NSI) was one of the first registrars, and today companies like PowerHoster.com offer domain registration in addition to many other Web site and domain management services.
Right now, We can register Hundreds of TLDs. We can register popular domain names, international domain names, and regional domain names and country domain names.
Domain Names work by linking with a DNS ( Domain Name Servers), The DNS searches for the root DNS and local DNS to find the best way to your domain name. If you want to see how domain name work, please click here. With PowerHoster, you’re guaranteed to find the perfect domain name that will help you bring your business success. A variety of domains are available to be registered quickly and easily, and at the best prices. Millions of satisfied customers and over four million registered domain names speak for themselves!
What is cheap web hosting ?
What To Expect From a Cheap Hosting Provider
Before I dive into what each provider offers and tell you all about their pros and cons, let me explain to you what affordable hosting providers normally offer.
There are several types of hosting (e.g. VPS or dedicated hosting), but the most economical one is shared hosting. It’s called shared because you share a server (and its resources) with other clients (websites). Similar to co-living in a flat, your rent will be cheaper but you may need to wait longer to access the shower.
Linux and Windows are the two favourite operating systems among web hosting servers – Linux being the most popular one and the one you most likely need (e.g. to use PHP and WordPress). But some providers also offer Windows-based hosting (e.g. to use Microsoft’s ASP.net). MySQL is normally the default database management system.
One way or another, a domain name will be given. Most providers will offer a free domain name for the first year (e.g. SiteGround or Bluehost), after that you’ll be prompted to pay for your domain name. Generally speaking, domain name registrars like Namecheap have better rates.
All hosting providers come with a control panel where you can manage your settings (e.g. choosing a PHP version) and access the hosting features (e.g. backups). Most affordable hosting plans use cPanel as a visual interface to manage your hosting. However, others like DreamHost have their own solutions (previous screenshot).
Every web host will have some kind of support, as we’ll see later on, this is a crucial aspect when choosing a hosting provider as it can save time and money.
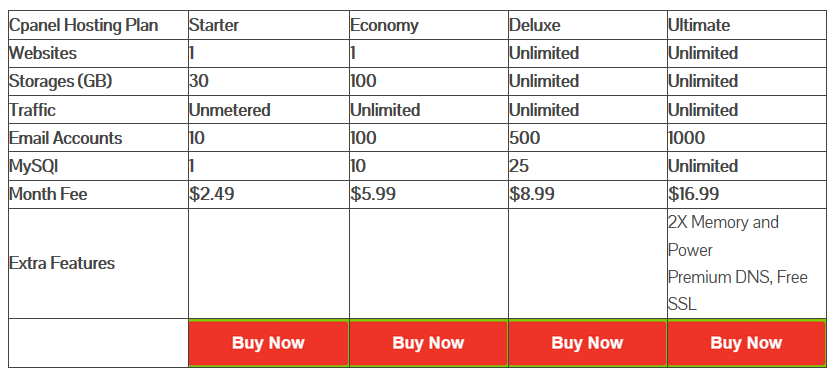
There are many types of affordable shared hosting services, but you can expect to pay between $7 to $30 a month after renewal – big discounts are often offered during the first term.
How to choose cheap web hosting ?
-
- Storage & bandwidth
Most quality hosts now come with unlimited storage, but some still have a 5GB limit or less.
-
- How many addon domains?
Most web hosts should give you space for up to 25 additional domains, but we’ve seen poor options that only give you one, or even none at all.
-
- How many email addresses can you create?
Some hosts don’t include a single email address in their package.
-
- What control panel do they use?
The control panel user experience can make or break a web host for me. Check if they use cPanel, Vdeck or a customized alternative. Pick the one you feel most comfortable with. (Pro tip: if you’re unfamiliar with their control panel, ask for a demo.)
-
- Do they support pre-installed website scripts?
Check if they support WordPress, Drupal, Joomla installation. If you need any specialised features like PHP or ecommerce integration, make sure they support that too.
are there any hidden catches in their terms-of-service?
Most web hosts use strong marketing language, like ‘unlimited storage and bandwidth’ or ‘unlimited CPU’. Unfortunately even ‘unlimited’ has a limit! And you’ll find it in the web host’s terms of service.
In some cases, web hosts reserve the right to suspend or even disconnect a website that overloads these limits.
Below are some real life examples from reputable web hosts that show these restrictions: PowerHoster Cheap Domain Name Register